Grounded in Research. Proven in Practice.
The Delivering SMARTER Intervention (DSI) program is built on the Science of Reading and supported by independent research validating its effectiveness in improving literacy outcomes for students across K–12.
The Science Behind DSI
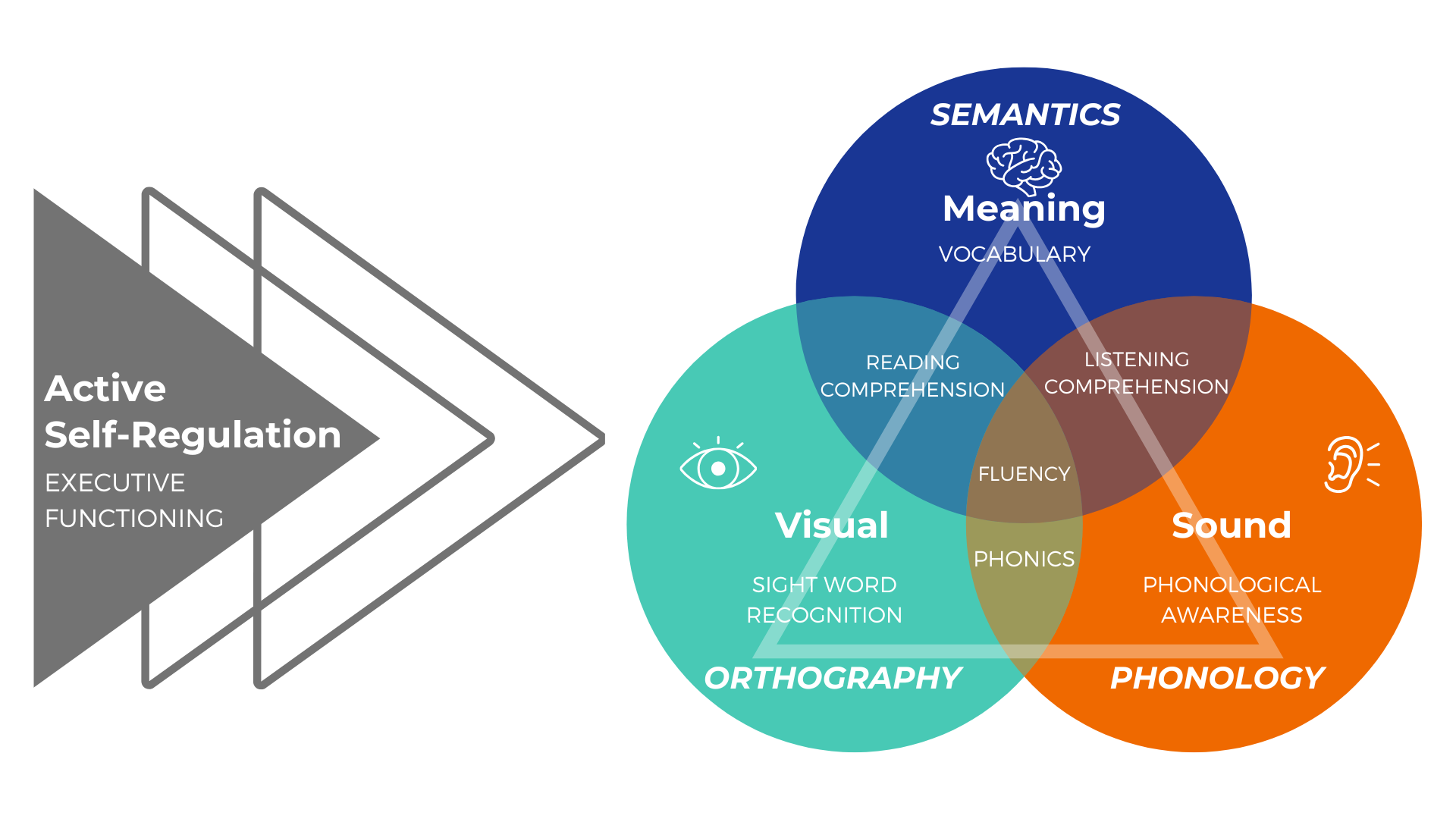
The Five Core Components of Reading
DSI provides systematic instruction in all five core components identified by the National Reading Panel (2000):
Phonological Awareness, Phonics, Vocabulary, Fluency, and Comprehension designed to support the cognitive process of reading and writing.
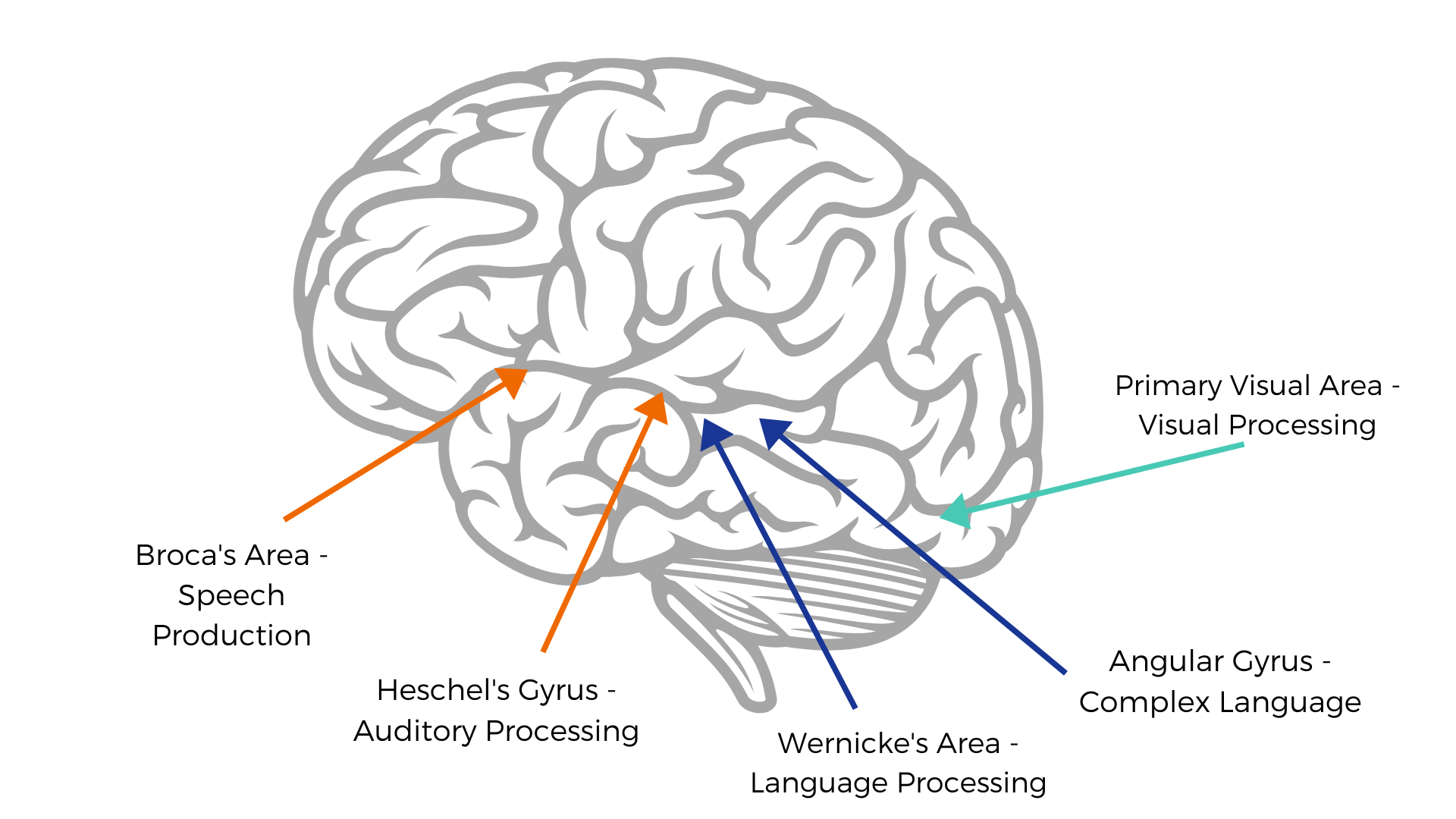
The Literacy Processing Triangle
Reading and writing rely on the interaction of phonology (sound), orthography (print), and semantics (meaning). DSI explicitly targets these neural pathways to develop efficient literacy processing.
From the Simple View to the Active View of Reading
DSI instruction builds both word recognition and language comprehension while integrating executive function and self-regulation, consistent with the “Active View of Reading” (Duke & Cartwright, 2021).
Independent Efficacy Study by the University of Denver
Sample: 81 students (ages 6–18), 78% diagnosed with dyslexia
Duration: 6–12 months of Delivering SMARTER Reading & Writing intervention
Outcome Measures:
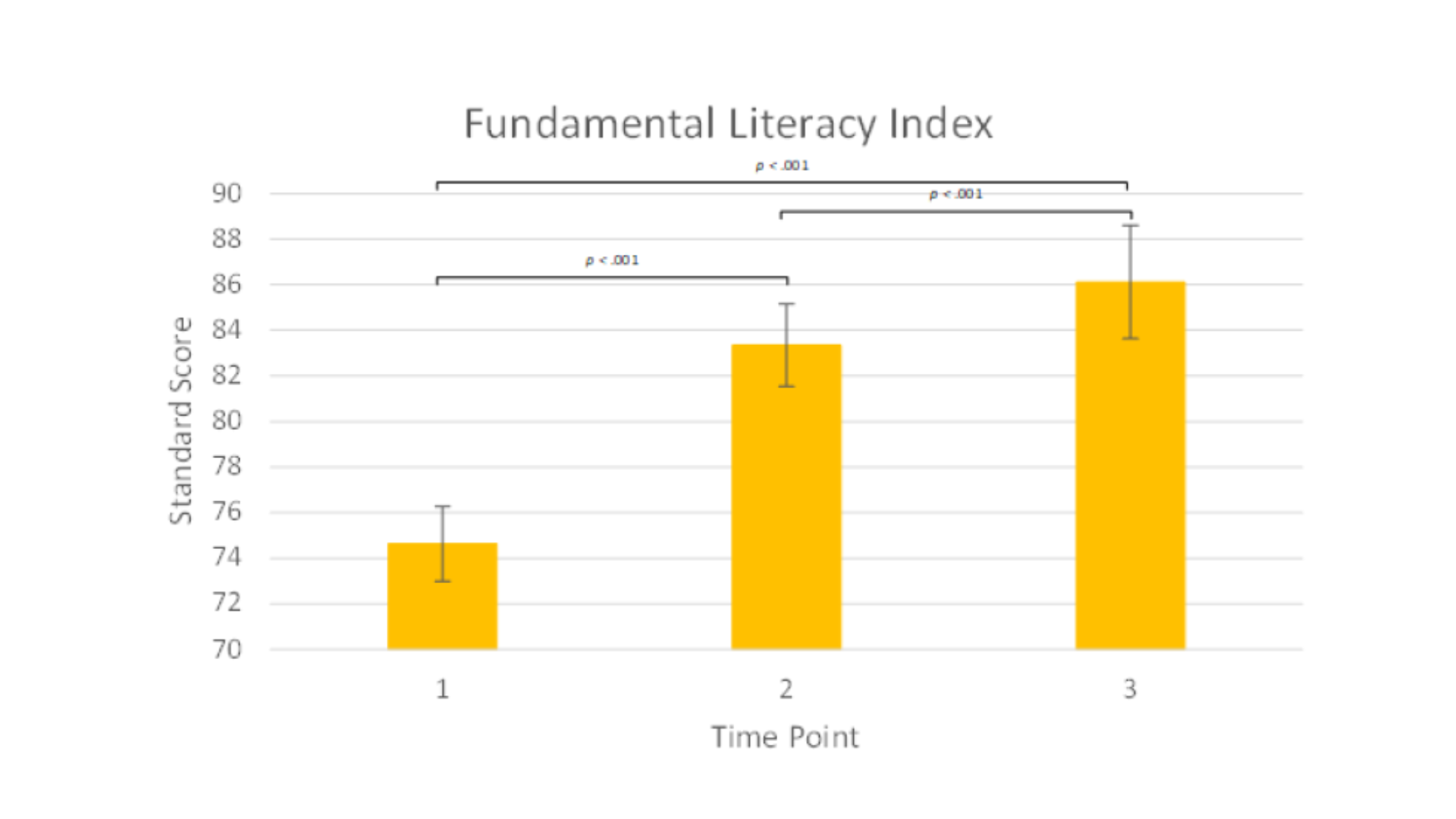
Word Identification & Spelling Test (WIST) – Fundamental Literacy Index
Gray Oral Reading Test, Fifth Edition (GORT-5) – Oral Reading Index
Results:
WIST: +8 SS points (large effect size, d = 1.01) after 6 months
GORT-5: +4 SS points (moderate effect size, d = 0.42) after 9 months
Conclusion:
Students made statistically significant gains in literacy and fluency within the first six months of intervention, with continued growth observed over time.
Key Research & Research Base
Phonological Awareness & Word Recognition
Kilpatrick (2016). Equipped for Reading Success.
Ehri (2020). The Science of Learning to Read Words.
Fluency & Comprehension
Wolf (2007). Proust and the Squid.
Hudson et al. (2009). The Complex Nature of Reading Fluency.
Vocabulary & Language Development
Beach et al. (2015). Teaching Academic Vocabulary to Adolescents with Learning Disabilities.
Duke & Cartwright (2021). The Active View of Reading.